niab ospf tutorial
lab
Lab diagram
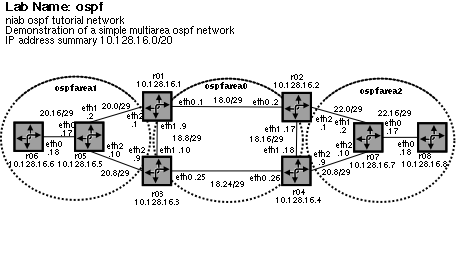
Lab aim
This is the second of five labs that make up the niab tutorial.
To complete
the tutorial, it is recommended that you follow the lab-guides in this
order.
demo-lab-guide: Introduction to using niab.
ospf-lab-guide: OSPF
tutorial.
<< You are here !
bgp-lab-guide: BGP tutorial.
ent1-lab-guide: DNS, email, web tutorial.
isp1-lab-guide: Use external lab connections.
Covers the configuration and support of the OSPF routing protocol.
Lab overview
This is the second of five labs that make up the niab tutorial.
To complete
the tutorial, it is recommended that you follow the lab-guides in this
order.
demo-lab-guide: Introduction to using niab.
ospf-lab-guide: OSPF
tutorial.
<< You are here !
bgp-lab-guide: BGP tutorial.
ent1-lab-guide: DNS, email, web tutorial.
isp1-lab-guide: Use external lab connections.
Covers the configuration and support of the OSPF routing protocol.
Lab instructions
1) Restore
the lab
We perform
the same steps as described in the 'demo' tutorial.
- start the
lab
[ncarter:~/niab-labs/ospf]>niab
start
[ncarter:~/niab-labs/ospf]>
- wait for
nodes to boot (tail log/*.log file to view boot progress)
- restore the
lab configuration
Only attempt
this once all the nodes are fully booted.
[ncarter:~/niab-labs/ospf]>niab
restore
niab: node
'r01' config restored from ./node-configs/r01
niab: node
'r02' config restored from ./node-configs/r02
niab: node
'r03' config restored from ./node-configs/r03
niab: node
'r04' config restored from ./node-configs/r04
niab: node
'r05' config restored from ./node-configs/r05
niab: node
'r06' config restored from ./node-configs/r06
niab: node
'r07' config restored from ./node-configs/r07
niab: node
'r08' config restored from ./node-configs/r08
[ncarter:~/niab-labs/ospf]>
- stop the lab
[ncarter:~/niab-labs/ospf]>niab
stop
[ncarter:~/niab-labs/ospf]>
- wait for
nodes to stop
- start the
lab
Only attempt
this once all nodes have stopped.
[ncarter:~/niab-labs/ospf]>niab
start
[ncarter:~/niab-labs/ospf]>
- wait for
nodes to boot (tail *.log file to view boot progress)
2) Connect to
node r01, and log in as user root.
If you are
running X-Windows:
[ncarter:~/niab-labs/ospf]>niab
term r01
[ncarter:~/niab-labs/ospf]>
An xterm
connected to r01, displaying a login prompt, will appear.
If you are
not running X-Windows:
- use 'niab
nodes' command to find out which tcp port is bound to r01
- telnet to
the tcp port
3) Check
connectivity
All routers
in this lab should be able to ping each other.
- ping each
remote router r02 - r08
r01:~# ping
-c 2 r02
PING r02
(10.128.16.2): 56 data bytes
64 bytes from
10.128.16.2: icmp_seq=0 ttl=64 time=6.8 ms
64 bytes from
10.128.16.2: icmp_seq=1 ttl=64 time=1.9 ms
--- r02 ping
statistics ---
2 packets
transmitted, 2 packets received, 0% packet loss
round-trip
min/avg/max = 1.9/4.3/6.8 ms
r01:~#
Repeat for
r03 - r08
If any of
these pings fail then its time to start troubleshooting.
4) View r01
OSPF configuration
r01:~# telnet
localhost ospfd
Password:
zebra
r01-ospfd>
enable
Password:
zebra
r01-ospfd# sh
run
...
router ospf
ospf
router-id 10.128.16.1 << router-id is set
to dummy0 address
passive-interface
dummy0 << do not send hello
packets out of dummy0
network
10.128.16.1/32 area 0 << dummy0 interface is part of area 0
network
10.128.18.0/29 area 0 << 2 x core links are part of area 0
network
10.128.18.8/29 area 0
network
10.128.20.0/29 area 1 << Link to area 1 is part of area 1
area 1
range 10.128.20.0/23 << Summarise area1 address
range
...
r01-ospfd#
5) View r01
hello packets
- turn on
terminal monitoring (console messages are now also copied to this
terminal)
r01-ospfd#
term monitor
- turn on
ospf hello debug
r01-ospfd#
debug ospf packet hello
... ospf
hello packets sent / received between r01 and r02 ...
2004/06/16
10:35:15 OSPF: Hello received from [10.128.16.2] via
[eth0:10.128.18.1]
2004/06/16
10:35:15 OSPF: src [10.128.18.2],
2004/06/16
10:35:15 OSPF: dst [224.0.0.5]
2004/06/16
10:35:17 OSPF: Hello sent to [224.0.0.5] via [eth0:10.128.18.1].
....
- turn off
ospf hello debug
r01-ospfd# no
deb ospf packet hello
6) View
Router LSA for r02
r01-ospfd# sh
ip ospf database router adv-router 10.128.16.2
...
Router Link States (Area (0.0.0.0))
LS
age: 1490 << Age of LSA, will eventually trigger LSA refresh
Options: 2
Flags:
0x1 : ABR
LS
Type: router-LSA
Link
State ID: 10.128.16.2
Advertising Router: 10.128.16.2
LS Seq
Number: 80000004 << No change if network is stable (until
timeout)
Checksum: 0xcad8
Length: 60
Number of Links: 3
Link connected to: Stub
Network
<< Stub as this is dummy0
(Link ID) Network/subnet number: 10.128.16.2
(Link Data) Network Mask: 255.255.255.255
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metric: 10 << metric for this link is 10 (default)
Link connected to: a Transit Network
(Link ID) Designated Router address: 10.128.18.2 <<
r02 is DR
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 10.128.18.2 <<
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metric: 10
Link connected to: a Transit Network
(Link ID) Designated Router address: 10.128.18.18 << r04 is
DR
(Link Data) Router Interface address: 10.128.18.17 <<
Number of TOS metrics: 0
TOS 0 Metric: 10
7) View
summary LSA for r08 dummy0
r01-ospfd# sh
ip ospf database summary 10.128.16.8
OSPF Router with ID (10.128.16.1)
Summary Link States (Area (0.0.0.0))
LS
age: 457
Options: 2
LS
Type: summary-LSA
Link
State ID: 10.128.16.8 (summary Network Number) << r08 dummy0
Advertising Router: 10.128.16.2 << r02 is summarising
into area0
LS Seq
Number: 80000002
Checksum: 0x32cc
Length: 28
Network Mask: /32 << dummy addresses are
configured as /32 host address
TOS: 0 Metric: 30
LS
age: 242
Options: 2
LS
Type: summary-LSA
Link
State ID: 10.128.16.8 (summary Network Number)
Advertising Router: 10.128.16.4 << r04 is summarising
into area0
LS Seq
Number: 80000002
Checksum: 0x26d6
Length: 28
Network Mask: /32
TOS: 0 Metric: 30
Summary Link States (Area (0.0.0.1))
LS
age: 258
Options: 2
LS
Type: summary-LSA
Link
State ID: 10.128.16.8 (summary Network Number)
Advertising Router: 10.128.16.1 << r01 is summarising into
area1
LS Seq
Number: 80000002
Checksum: 0x9c59
Length: 28
Network Mask: /32
TOS: 0 Metric: 40
LS
age: 2346
Options: 2
LS
Type: summary-LSA
Link
State ID: 10.128.16.8 (summary Network Number)
Advertising Router: 10.128.16.3 << r03 is summarising into
area1
LS Seq
Number: 80000001
Checksum: 0x9262
Length: 28
Network Mask: /32
TOS: 0 Metric: 40
8) View r01
ospf route to r08
r01-ospfd# sh
ip ospf route
============
OSPF network routing table ============
...
N IA
10.128.16.8/32 [40] area:
(0.0.0.0)
via 10.128.18.2, eth0
...
r01-ospfd#
9) View r01
zebra route to r08
r01-ospfd#
exit
Connection
closed by foreign host.
r01:~# telnet
localhost zebra
...
Password:
zebra
r01-zebra>
sh ip route 10.128.16.8
Routing entry
for 10.128.16.8/32
Known
via "ospf", distance 110, metric 40, best
Last
update 00:50:01 ago
*
10.128.18.2, via eth0
10) View r01
kernel route to r08
r01-zebra>
exit
Connection
closed by foreign host.
r01:~#
netstat -r | grep r08
r08
10.128.18.2 255.255.255.255
UGH 0
0 0 eth0
r01:~#
11) Check
OSPF reconverges after link failure
- shutdown
r01 eth0
[Use zebra to
shutdown the 'zebra' interface, do not use the 'ifconfig' command
to shutdown
the 'kernel' interface. Other processes are using the 'kernel'
interface, so
the 'ifconfig' command will fail.]
r01:~# telnet
localhost zebra
...
Password:
zebra
r01-zebra>
en
Password:
zebra
r01-zebra#
conf t
r01-zebra(config)#
int eth0
r01-zebra(config-if)#
shutdown
r01-zebra(config-if)#
end
r01-zebra#
- check int
eth0 is down
r01-zebra# sh
int eth0
Interface eth0
index
6 metric 1 mtu 1500 <BROADCAST,ALLMULTI,MULTICAST> <<
'UP' is missing
HWaddr: fe:fd:0a:80:12:01
inet
10.128.18.1/29 broadcast 10.255.255.255
input packets 399, bytes 27568, dropped 0, multicast packets 0
input errors 0, length 0, overrun 0, CRC 0, frame 0, fifo 0, missed 0
output packets 407, bytes 33854, dropped 0
output errors 0, aborted 0, carrier 0, fifo 0, heartbeat 0, window 0
collisions 0
- check
alternate route has been found
r01-zebra# sh
ip route 10.128.16.8
Routing entry
for 10.128.16.8/32
Known
via "ospf", distance 110, metric 50, best
Last
update 00:02:41 ago
*
10.128.18.10, via eth1 << route is now via eth1
(r03)
12) Have a
play ! If you completely break the lab, you can easily restore the
original
setting using the 'niab restore' command on the host system.
13) Stop the
lab
[ncarter:~/niab-labs/ospf]>niab
stop
[ncarter:~/niab-labs/ospf]>
14) Move on
to the next tutorial lab (bgp)
Appendix 1:
IP Subnetting (ospf tutorial lab)
10.128.16.0/20
- Lab summary
10.128.16.0/24 - 256 x /32 dummy0
10.128.17.0/24 - Unassigned
10.128.18.0/24 - 32 x /29 Area 0 LAN links
10.128.19.0/24 - 64 x /30 Area 0 WAN links
10.128.20.0/24 - 32 x /29 Area 1 LAN links
10.128.21.0/24 - 64 x /30 Area 1 WAN links
10.128.22.0/24 - 32 x /29 Area 2 LAN links
10.128.23.0/24 - 64 x /30 Area 2 WAN links
10.128.24.0/24 - 10.128.31.0 - unassigned
